Up to 10 cash back The angiotensin AT2 receptor stimulates protein tyrosine phosphatase activity and mediates inhibition of particulate guanylate cyclase. However Ichikawa Hypertens Res 2001.

Schematic Showing The Mechanism Of Action Of Angiotensin With Download Scientific Diagram
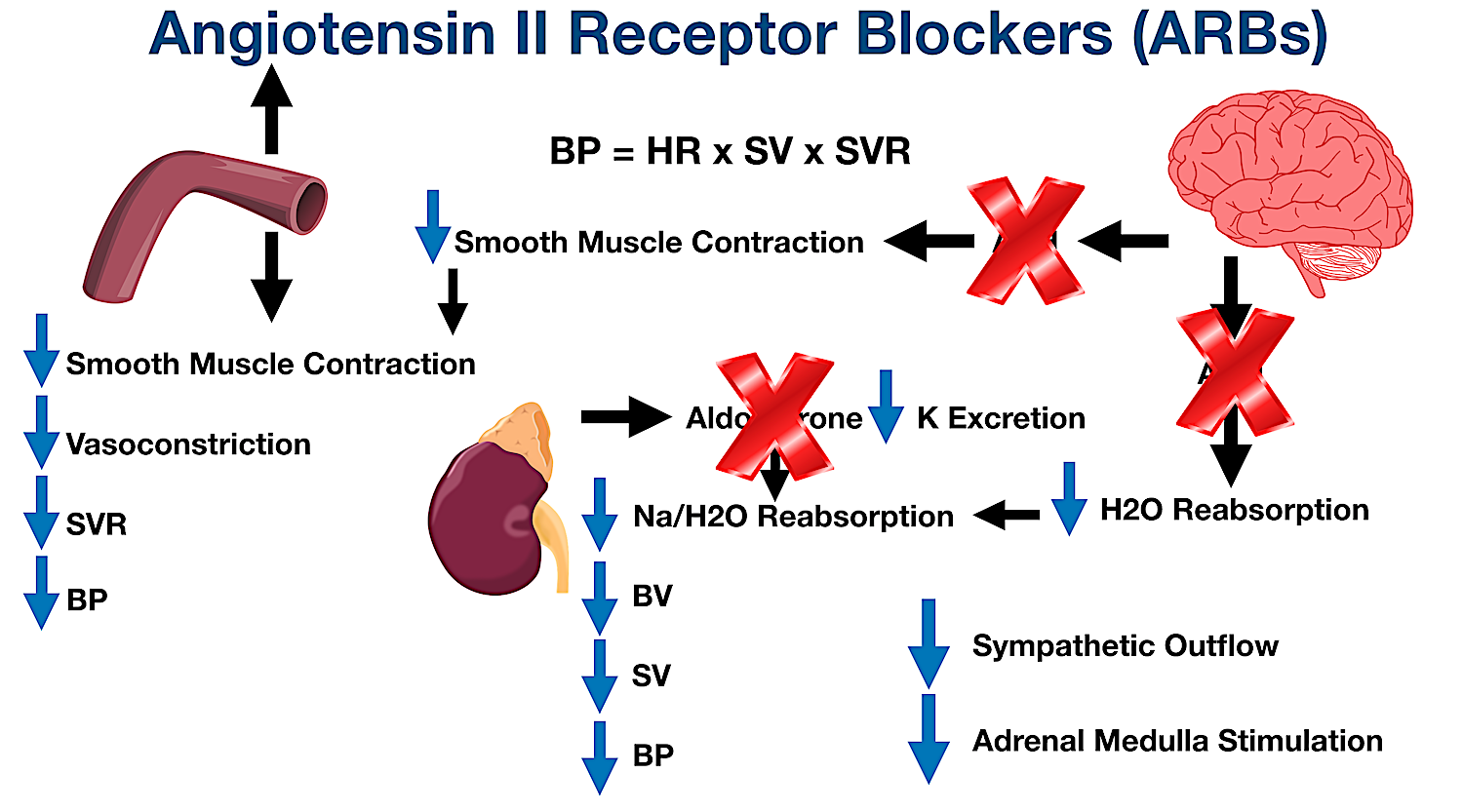
Summary of the pharmacological action mechanism of action and adverse effects of angiotensin II receptor blockers ARBs.
Angiotensin 2 receptor blocker mechanism of action. Angiotensin receptor blockers are one of several drug classes that act by hindering activity of the renin-angiotensin axis. Angiotensin receptor blockers act by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the angiotensin type 1 receptor but not the angiotensin type 2 receptor. Asked Oct 27 2016 in Nursing by Common.
That is they block the activation of angiotensin II AT 1 receptors. PharmacologyMechanism of Action. Angiotensin II receptor antagonistsblockers ARBs antagonize angiotensin II at the AT 1 receptors in tissues such as smooth muscle and the adrenal gland.
Blocking AT1 receptors which prevent angiotensin from raising blood pressure 4. Angiotensin II receptors19Angiotensin II type 1 AT 1 recep- tors are selectively inhibited by losartan and are sensitive to dithiothreitol whereas type 2 AT2 receptors are inhibited by PD 123177 and related compounds but are insensitive to dithiothreitol. Angiotensin is a chemical in your body that narrows your blood vessels.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers ARBs are widely used for the treatment of hypertension. These substances are AT 1-receptor antagonists. Compounds in this class are as effective as most other antihypertensive drug classes in.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers ARBs are medications that block the action of angiotensin II by preventing angiotensin II from binding to angiotensin II receptors on the muscles surrounding blood vessels. Blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II 3. Mechanism of action ARBs including candesartan irbesartan losartan telmisartan and valsartan antagonize the effects of angiotensin II at the AT1 receptor.
He lowered his eyes and said lightly Well of course I trust Mrs. Following self restriction diuretic therapy or renal artery stenosis but ARBs also lower blood pressure when there is normal or low activity of the renin-angiotensin system. Telmisartan is an angiotensin-II receptor antagonist ARB used in the treatment of hypertension.
It is believed that treatment with an ARB increases the level of plasma angiotensin II Ang II because of a lack of negative feedback on renin activity. The direct action of angiotensin II on surrounding vessel walls is facilitated by binding to the G-protein-coupled angiotensin II receptor type 1 AT-1 on vascular smooth muscle cells which stimulates Ca2calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of myosin and causes smooth muscle contraction that results in vasoconstriction Label 1. The angiotensin II receptor blockers ARBs represent a newer class of antihypertensive agents.
This narrowing can increase your blood pressure and force your heart to work harder. Angiotensin receptor blockers ARBs work in the body to lower blood pressure by which mechanism of action. Ferrario CM Jessup J Chappell MC Averill DB Brosnihan KB Tallant EA et al.
Their mechanism of action however is very different from ACE inhibitors which inhibit the formation of angiotensin II. Angiotensin II receptor blockers help relax your veins and arteries to lower your blood pressure and make it easier for your heart to pump blood. 2 Reduction in blood pressure secondary to vasodilation following angiotensin receptor blockade is greatest when the renin-angiotensin system is activated eg.
ARBs are receptor antagonists that block type 1 angiotensin II AT 1 receptors on bloods vessels and other tissues such as the heart. These receptors are coupled to the Gq-protein and IP 3 signal transduction pathway that stimulates vascular smooth muscle. Angiotensin 2 receptor blockers ARBs nursing NCLEX pharmacology review for the cardiovascular systemAngiotensin II receptor blockers mechanism of action w.
Mechanisms by which angiotensin-receptor blockers increase ACE2. Competitive inhibition of ACE results in a reactive. Generally angiotensin-II receptor blockers such as telmisartan bind to the angiotensin-II type 1 receptors with high affinity causing inhibition of the action of angiotensin II on vascular smooth muscle ultimately leading to a reduction in arterial blood pressure.
Angiotensin 2 receptor blocker antagonist pharmacology review. The ARBs were developed to overcome several of the deficiencies of ACE inhibitors. PubMed Article CAS Google Scholar 7.
Angiotensin II a potent vasoconstrictor is the primary vasoactive hormone of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system RAAS and plays an important role. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992 183 206211. Angiotensin receptor blockers act by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the angiotensin type 1 receptor but not the angiotensin type 2 receptor.
Normally angiotensin II increases sodium and water reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the nephron. As a result blood vessels enlarge dilate and blood pressure is reduced. After thinking for a angiotensin receptor blockers mechanism of action moment Xue Bin said If the two conditions proposed by the young lady don t want to be Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Mechanism Of Action considered then there is only one way to invest money to stabilize the situation.
AT 1 receptors are found in smooth muscle cells of vessels cortical cells of the adrenal gland and adrenergic nerve synapses. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Mechanism of Action Renin secretion is by the juxtaglomerular cells of the kidneys and catalyzes the conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I ATI in the liver.
Angiotensin receptor blockers ARBs work in the body to lower blood pressure by which mechanism of action. Mechanism of action vs ACE inhibitors how ARBs work side effects example medications ind. In rodents AT1receptors have been further subdivided into AT1Aand AT1B.
ATI is converted to angiotensin II ATII by angiotensin-converting. Ferrario CM Ahmad S Groban L. Blocking angiotensin II receptors with an ARB means less sodium and water reabsorption which will decrease blood volume which will decrease stroke volume which will decrease blood pressure.
Compounds in this class are as effective as most other antihypertensive drug classes in reducing blood pressure in the patient with hypertension. Their mechanism of action differs from that of the angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors which also affect the reninangiotensin system. Inhibiting the stimulation of aldosterone secretion 2.
Asked Oct 27 2016 in Nursing by Common 1.
Angiotensin Ii Receptor Blockers Arbs Indications Side Effects Mechanism Of Action Examples Ezmed
Tidak ada komentar