2 overactivity of the reninangiotensin system as observed in cardiovascular diseases and the lack of balance. These have included the recognition that angiotensin Ang- 1-7 is a biologically active product of the RAS cascade.

Mas Receptor Activation Contributes To The Improvement Of Nitric Oxide Bioavailability And Vascular Remodeling During Chronic At1r Angiotensin Type 1 Receptor Blockade In Experimental Hypertension Hypertension
In this study renal deficiency for Mas diminished renal damage in models of renal insufficiency as unilateral ureteral obstruction and ischemiareperfusion injury while the.

Angiotensin 1-7 mas receptor. The receptor for Ang- 1-7 the MasR has been detected in the hippocampus amygdala cortex hypothalamus and brain stem 27. We demonstrate that genetic deletion of the G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the Mas protooncogene abolishes the binding of Ang- 17 to mouse kidneys. As well as cell proliferation survival matrix-cell interactions.
In the present work we investigated the hypothesis that the anti-inflammatory action mediated by both receptors results from MasR-D2R heteromerization. Angiotensin-1-7 through receptor Mas mediates endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation via Akt-dependent pathways Angiotensin-1-7 Ang-1-7 causes endothelial-dependent vasodilation mediated in part by NO release. Ang-17 by interacting with the G protein-coupled receptor Mas may also have important biological activities.
Therapeutic angiotensin 1-7 may inhibit cyclooxygenase 2 COX-2 and the production of proinflammatory prostaglandins and may activate the angiotensin- 1-7 receptor Mas resulting in. These four receptors together regulate cardiovascular hemodynamic neurological renal and endothelial functions. Many studies have now shown that Ang-1-7 by acting via Mas receptor exerts inhibitory effects on inflammation and on vascular and cellular growth mechanisms.
Angiotensin 1-7 with proven performance. Ang-17 binds to Mas-transfected cells and elicits arachidonic acid release. Angiotensin-1-7 Ang-1-7 binds and activates the Mas receptor MasR.
Angiotensin Ang 1-7 is the endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas a receptor R associated with cardiac renal and cerebral protective responses. Angiotensin-1-7 binds to the G-protein-coupled Mas receptor MasR to oppose deleterious effects elicited by angiotensin II Savergnini et al 2010. We hypothesized that Ang-1-7 inhibits CIBP by targeting MasR in a murine model of breast CIBP.
Action of the ACE on angiotensin 1-9. Ang-1-7 has also been shown to reduce key signalling pathways and molecules thought to be relevant for fibrogenesis. Activation of the MAS receptor by angiotensin-1-7 in the renin-angiotensin system mediates mesenteric vasodilatation in cirrhosis In the splanchnic vessels of patients and rats with cirrhosis increased levels of ACE2 appear to increase production of Ang-1-7 which leads to activation of MasR and splanchnic vasodilatation in rats.
However the molecular mechanisms involved in endothelial NO synthase eNOS activation by Ang-1-7 remain unknown. Angiotensin-1-7 and the receptor Mas were localized to primordial primary secondary and antral follicles stroma and corpora lutea of reproductive-age ovaries. Solubility and Storage Guidelines.
Collectively these findings identify Mas as a functional receptor for Ang-17 and provide a clear molecular basis for the physiological actions of this biologically active peptide. Recent advances have improved our understanding of the renin-angiotensin system RAS. Postmenopausal women expressed both the peptide and its receptor in the ovarian stroma.
Ad Peer-reviewed Papers Cited Independent Validation Find Protocols Technical Support. Angiotensin-1-7 was detectable in FF meanSE. Angiotensin 1-7 synthesis pathway Possible synthesis pathways Action of the neprilysin on angiotensin I or angiotensin II.
Ang 1-7 binds and activates the G-protein coupled receptor Mas receptor leading to opposite effects of those of Ang II. Therapeutic Angiotensin- 1-7 is a synthetic heptapeptide identical to endogenous angiotensin- 1-7 with vasodilator and antiproliferative activities. Ang- 1-7 acting through the g protein-coupled receptor gpcr mas releases no and prostaglandins causing vasodilation inhibition of cell growth and opposition of at 1 r-mediated ang ii vasoconstrictor and proliferative effects.
Within the hypothalamus and brainstem MasR is preferentially located in areas related to the control of cardiovascular function such as NTS CVLM and RVLM and in the hypothalamic PVN and SON 27. While these are G-protein coupled receptors GPCRs the in vivo angiotensin IV binding sites may be type 2 transmembrane proteins. Furthermore Mas-deficient aortas lose their Ang-17-induced relaxation response.
Angiotensin Ang 1-7 is the endogenous ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor Mas a receptor associated with cardiac renal and cerebral protective responses. Physiological evidence suggests that Mas R undergoes agonist-dependent desensitization but the underlying molecular mechanism regulating R activity is unknown. Ang angiotensin 17 MasR Mas receptor and D2R dopamine D2 receptor stimulation is coupled to anti-inflammatory responses.
Action of the prolyl endopeptidase on angiotensin I. The oncogene product MAS is a putative receptor for Ang 17. Angiotensin 1-7 Ang 1-7 initially believed to be an inactive metabolite of AngII was later found to be a ligand for the orphan G proteincoupled receptor Mas and to induce signaling in cells transfected with Mas.
Accordingly Mas -deficient mice completely lack the antidiuretic action of Ang- 17 after an acute water load. It has been shown to exert anti-hypertensive and cardioprotective actions through. Physiological evidence suggests that Mas receptor MasR undergoes agonist-dependent desensitization but the underlying molecular mechanism regulating receptor activity is unknown.
Tissues of Mas knockout mice lack of Ang 1-7 binding and show blunted responses to the Ang 1-7 in vitro. The identification of the ACE homologue ACE2 which forms Ang- 1-7 from Ang II and the GPCR Mas as an Ang- 1-7 receptor have provided the necessary biochemical and. Angiotensin-1-7MasR activation modulates inflammatory signaling after acute tissue insult yet no studies have investigated whether Ang-1-7MasR play a role in CIBP.
Angiotensin Ang II mediates pathophysiologial changes in the kidney.
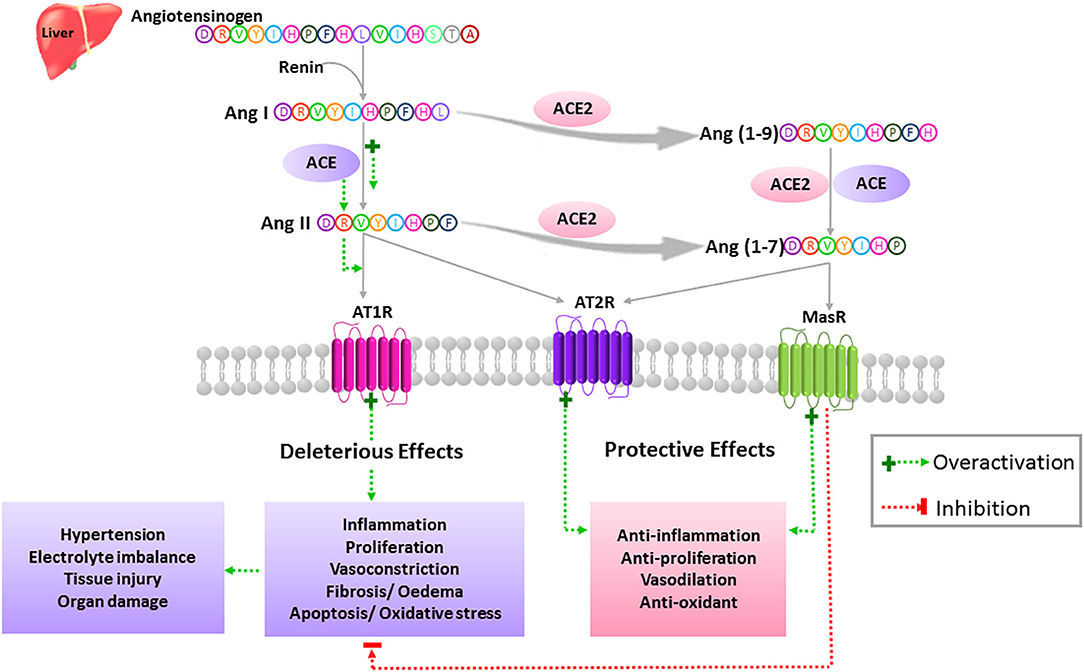
Frontiers Combination Of Angiotensin 1 7 Agonists And Convalescent Plasma As A New Strategy To Overcome Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2 Ace2 Inhibition For The Treatment Of Covid 19 Medicine
Tidak ada komentar