Diagnostic consideration was given to neurogenic tumors and neoplasms of parotid originThe patient ultimately underwent superficial parotidectomy and the tumor was found superficial and extrinsic to the proximal facial nerve trunk but extended into the stylomastoid. After exiting the stylomastoid foramen it courses inferiorly and slightly laterally for 3-5 mm then turns more acutely laterally to pass above and in front of the posterior belly of the digastric muscle.
Growth Of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Of The Parotid During Pregnancy A Case Report
Slowly progressive peripheral facial nerve palsy may be due to parotid cancer and imaging should be employed whenever this occurs clinically.

Stylomastoid foramen parotid mas. They should be kept in the differential diagnosis of parotid swellings though it is very difficult to make a diagnosis of parotid schwannoma preoperatively. The chorda tympani nerve is the largest branch of the facial nerve in the intrapetrous compartment. T1-weighted imaging showed the lesion as isointense to muscle and T2-weighted imaging revealed almost uniform hyperintensity.
Facial nerve management is a crucial component of parotid surgery. Herpes of tympanum and of external auditory meatus may occur. Hyperacusia due to effect on nerve branch to stapedius muscle.
Tumor recurrence with stylomastoid foramen involvement was observed in 1 case 3 years after surgery. TA the distal or external opening of the facial canal on the inferior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone between the styloid and mastoid processes. Foramina or foramens An opening or orifice as in a bone or in the covering of the ovule of a plant.
Details on which types of parotid tumors are more likely to affect facial nerve function and different prognostic predictors of return to function are evaluated. CN VII exits the temporal bone via the stylomastoid foramen which is between the mastoid and styloid processes and deep to the posterior belly of the digastric. The patient ultimately underwent superficial parotidectomy and the tumor was found superficial and extrinsic to the proximal facial nerve trunk but extended into the stylomastoid.
The stylomastoid foramen is a rounded opening at the inferior end of the facial canal. Almost immediately the nerve enters the parotid gland. It then turns anteriorly.
A clinical case of a patient with an asymptomatic parotid mass diagnosed as a. As the facial nerve trunk travels from the stylomastoid foramen to the parotid body it passes anterior to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle lateral to styloid process and the external carotid artery and posterior to the facial vein. It is located on the inferior surface of the petrous temporal bone between the base of the styloid process and the mastoid process of the temporal bone.
For ACC arising from the parotid gland with extensive PNI or frank tumor involvement along CN VII we recommend electively covering the stylomastoid foramen and the proximal course of VII in the temporal bone Figure 3 A 4344. It transmits the facial nerve and stylomastoid artery branch of posterior auricular artery. It is extremely rare to have an invasion of the stylomastoid foramen by facial nerve schwannomas arising from the extra-temporal portion of the nerve.
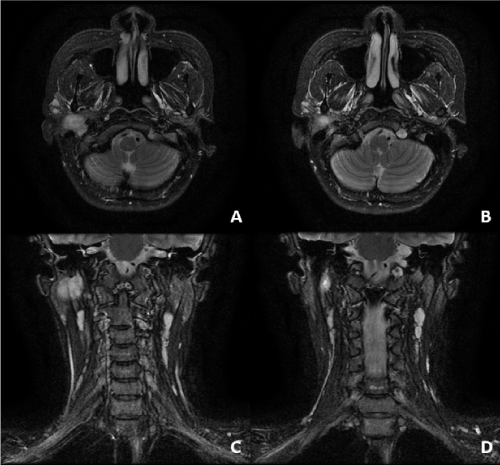
Imaging revealed a heterogeneous intraparotid mass with tumor extension into the stylomastoid foramen. 1 to 15 Tesla Sequences T2 weighted fluid attenuated inversion recovery These images are acquired in the axial plane perpendicular to the brainstem using a head coil. VII treated through stylomastoid foramen to base of skull Parotid with PNI 54 Gy Node negative ipsilateral cervical neck supraclavicular neck if necessary At risk nerves back to base of skull PTV CTV 3 mm with daily IGRT imaging July 23 2019 Stylomastoid foramen.
All symptoms of 4 plus loss of taste in anterior tongue and decreased salivation on affected side due to chorda tympani involvement. However this is not always the case because there have been case reports indicating that some benign tumors of the parotid gland can invade the stylomastoid foramen and through compression can cause paresis or paralysis. It transmits the facial nerve and stylomastoid artery.
When a parotid-region mass is due to metastases to parotid nodes computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging can help to identify parotid cancer or another etiology as a cause. An Unusual Position of Retromandibular Vein in Relation to Facial Nerve. At least 2 theories of tumorigenesis have been proposed for salivary gland neoplasms.
During parotid surgery there are important landmarks such as tragal pointer posterior belly of digastric stylomastoid foramen RMV and tympanomastoid suture line to identify facial nerve 5 6. By contrast in cases of microscopic PNI in early-stage disease of the parotid gland coverage should only include the. Declaration of patient consent.
Imaging revealed a heterogeneous intraparotid mass with tumor extension into the stylomastoid foramen. It splits from the facial nerve just before it exits via the stylomastoid foramen. Stylomastoid foramen - definition of stylomastoid foramen by The Free Dictionary.
Below stylomastoid foramen parotid gland. The anatomic relationship of the facial nerve is discussed as it exits the stylomastoid foramen and courses through the parotid gland. A Rare Case Report.
Every effort should be made to preserve the facial nerve functionRemoval of the mastoid process and careful dissection around the nerve in the stylomastoid foramen permits full exposure of the nerve as it passes through the facial canal. To study the brain and pons a slice thickness of 4 mm to 5 mm and a 256 matrix is used. The tumor was situated directly caudal to the stylomastoid foramen and protruded into it.
The facial nerve exits the skull base at the stylomastoid foramen. At the beginning of a parotidectomy start by mobilizing the tail of the parotid superiorly and retracting the anterior border of the. The facial nerve FN emerges extracranially through stylomastoid foramen and then proceeds anteriorly as covered by the parenchymal tissues of the parotid gland.
To expose the trunk of the facial nerve at the stylomastoid foramen the dissection passes down the avascular plane between the parotid gland and the external acoustic canal until the junction of the cartilaginous and bony canals. Anatomy of facial nerve Extratemporal Exits stylomastoid foramen 1cm superior to mastoid process and 1cm deep to lateral surface Indicated by tragal pointer junction of cartilaginous paortion of EAM with skull which is 5-6mm from stylomastoid foramen Other method of finding facial nerve trunk is to follow the tympanomastoid fissure junction. All symptoms of 3 and 4 plus pain behind ear.
MR imaging showed a well-circumscribed lesion with a diameter of 28 cm in the upper right parotid gland. After traveling anteriorly approximately 2 cm within the parotid the nerve divides at the posterior. Foraminal foraminous adj.
The surgical landmarks are important Figure 14. Diagnostic consideration was given to neurogenic tumors and neoplasms of parotid origin. The stylomastoid foramen SF and the parotid gland PG Technique.
Teristic course from the stylomastoid foramen through the parotid gland. The effect of certain tumors on facial nerve function is also characterized.

The Facial Nervethe Nerve That Is Injured With Bell S Palsy Is Cn Vii 7th Cranial Nerve It Originates In An Area Of Facial Nerve Bells Palsy Cranial Nerves

Tidak ada komentar