Approximately 10 to 15 of all infants are born through meconium-stained amniotic fluid MSAF of whom 3 to 9 develop meconium aspiration syndrome MAS Eight to 20 of infants born through MSAF are depressed and non-vigorous 12 with bradycardia inadequate respiratory effort and poor tone Every five years the. The incidence as a function of gestational age takes on a U-shaped curve with a nadir at 31.
Children Free Full Text Neonatal Respiratory Distress Secondary To Meconium Aspiration Syndrome Html
Oxygen should be administered early in any infant suspected of having inhaled meconium.
Meconium aspiration syndrome treatment guidelines. Defined as respiratory distress in the newborn due to the presence of meconium in the trachea. A randomized controlled trial Eur J Pediatr. Actions with meconium stained liquor a Labour and delivery care.
Meconium aspiration syndrome may cause severe respiratory distress in the newborn infant with an associated high morbidity and mortality. Meconium stained liquor during labour and thus are at increased risk of developing Meconium Aspiration Syndrome. The infants oro- and nasopharynx should be suctioned by the obstetrician prior to delivery of the shoulders.
It occurs exclusively in the immediate neonatal period. Also to NICU nurses advanced nurse practitioners and doctors to guide appropriate investigation and first line treatment where required. The aspiration of meconium stained amniotic fluid by the fetus can happen during antepartum or intrapartum periods and can result in airway obstruction interference with alveolar gas exchange.
Intrapartum and neonatal attributes. This document is only valid for the day on which it is accessed. A baby may release meconium due to potential stressors like.
Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is defined as respiratory distress in the newborn due to the presence of meconium in the trachea. Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is the aspiration of stained amniotic fluid which can occur before during or immediately after birth. If the baby is not vigorous defined as having a depressed respiratory effort or poor muscle tone place the baby on a.
A change in practice was supported in animal 13 and human 7111415 studies. Endotracheal suctioning for prevention of meconium aspiration syndrome. Soon after birth infants pr.
Another factor is a longer-than-usual. Int J Pediatr 20122012965159. The suggested target range for oxygen saturation is 91-95 per cent.
Meconium is sterile and does not contain bacteria. At delivery treatment may include. Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is the neonatal respiratory distress that occurs in a newborn in the context of MASF when respiratory symptoms cannot be attributed to another etiology.
Target PaO 2 60-90 mmHg. The use of oxygen has a risk to benefit equation just as for any other drug. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists makes the following recommendations.
Meconium-stained liquor and meconium aspiration. The question remained if there was sufficient evidence to recommend the empirical tracheal suctioning of nonvigorous infants with MSAF to reduce risk of meconium aspiration syndrome MAS or meconium-related morbidity or mortality. Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is a major cause of severe respiratory distress in newborns and the role of antibiotics in its management is not well defined.
Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is defined as respiratory distress in a newborn infant born through meconium-stained fluid whose symptoms cannot otherwise be explained. Authors Ashok Kumar 1 Preetam Kumar 2 Sriparna Basu 3 Affiliations 1 Neonatal Unit. Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is respiratory distress in a newborn baby caused by the presence of meconium in the tracheobronchial airways.
Resuscitation should follow the same principles for infants with meconium-stained. The length of time the baby was exposed. Meconium aspiration syndrome can sometimes occur when a baby is under stress due to low oxygen or an infection either in utero or during delivery.
Infants with meconium-stained amniotic fluid regardless of whether they are vigorous or not should no longer routinely. Description Meconium is the first intestinal discharge from newborns a viscous dark-green substance composed of intestinal epithelial cells lanugo mucus and intestinal secretions. Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is defined as respiratory distress in newborn infants born through meconium-stained amniotic fluid MSAF whose symptoms cannot be otherwise explained.
The Paediatric Resident SHO Registrar or NS-ANP should be called if there is thick meconium staining or light meconium plus fetal distress. MAS occurs in approximately 2-10 of infants born through meconium-stained fluid. If the baby is vigorous defined as havin a normal respiratory effort and normal muscle tone the baby may stay with.
Rossi EM Philipson EH Williams TG et al. Treatment in the delivery room 1. A systematic review and meta-analysis Journal of Perinatology 2016 36 S48S53.
Respiratory support in meconium aspiration syndrome. CK Natarajan et al Surfactant therapy and antibiotics in neonates with meconium aspiration syndrome. Infants born through meconium-stained amniotic fluid are at risk of developing meconium aspiration syndrome particularly in the presence of maternal and fetal risk factors.
Following suctioning of the oro- and nasopharynx by the obstetrician the infants oro- and nasopharynx should be. A chemical pneumonitis is believed to occur secondary to bile bile acids and pancreatic secretions contained in. Specific treatment for meconium aspiration will be determined by your childs doctor based on the following.
The degree of respiratory distress. 1 The spectrum of manifestations associated with meconium aspiration is broad ranging from mild distress to more severe respiratory failure. To determine the role of routine antibiotic therapy in the management of MAS.
Epub 2019 Oct 7. A tough extended labor and delivery may up the risk of passing meconium. The most recent guidelines are as follows 10 11.
The amount and thickness of the meconium. After excluding the possibility of sepsis 144 patients with MAS were randomised into two groups. MAS can present with varying degrees of severity from mild respiratory distress to life-threatening respiratory failure.
Suctioning of the upper airways nose mouth and throat.

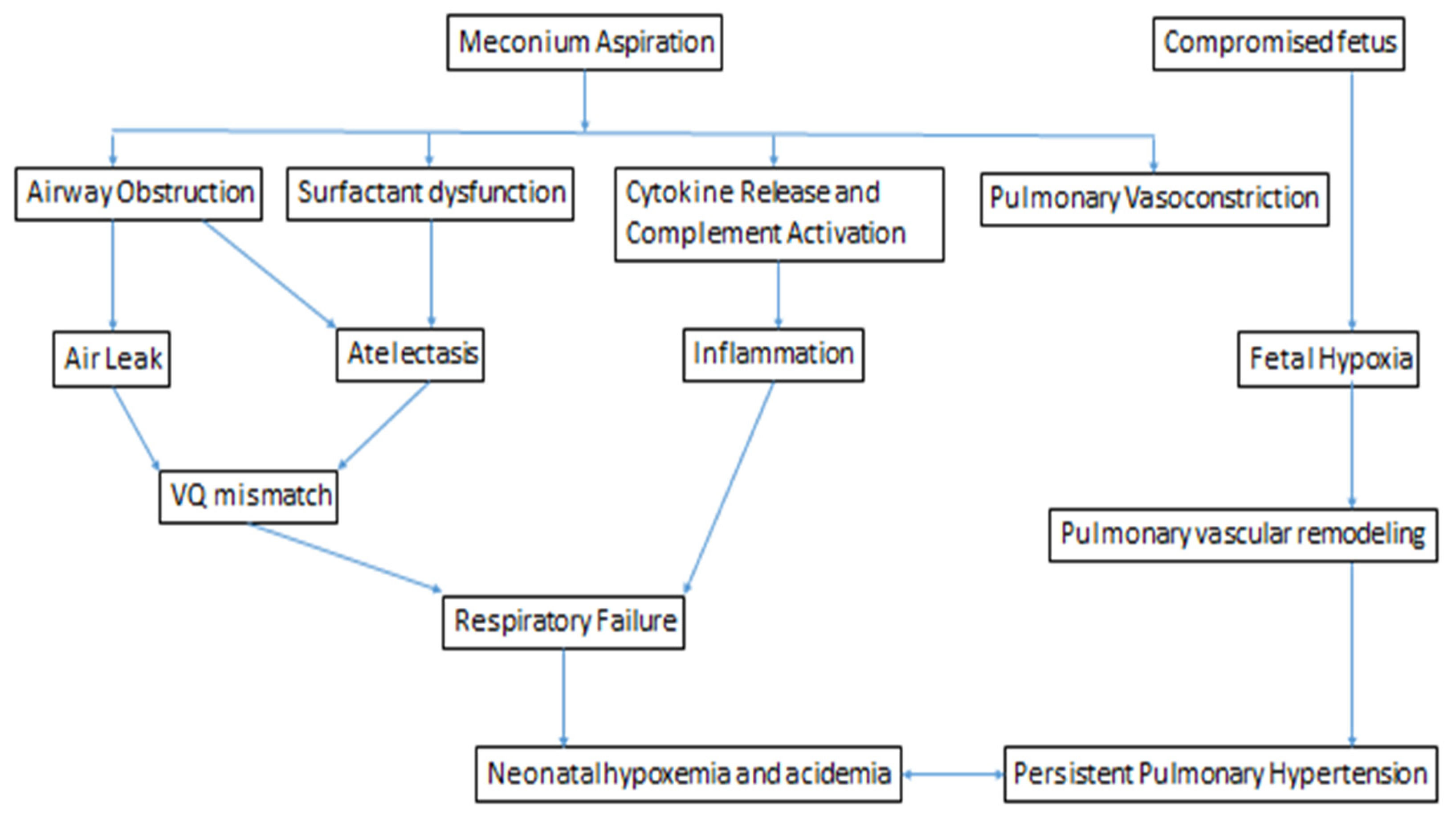
Pathophysiology Of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome From Fanaroff And Download Scientific Diagram
Tidak ada komentar