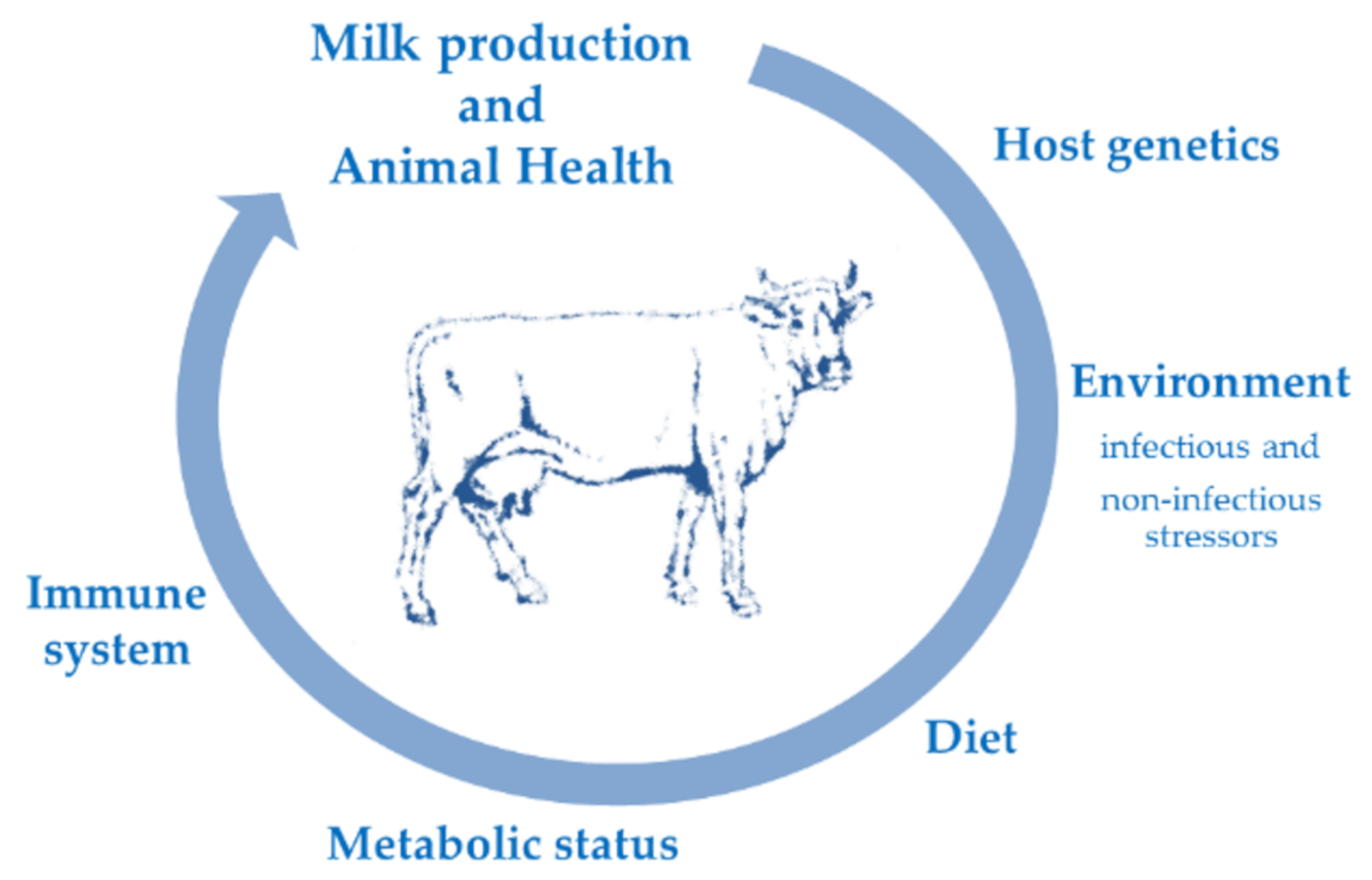
A number of bacteria mycoplasmas yeasts and fungi can cause clinical mastitis. Such stress can lock the flow of oxytocin the milk let down hormone and subsequently retaining of milk which is another predisposing factor in mastitis.
Animals Free Full Text The Role Of Innate Immune Response And Microbiome In Resilience Of Dairy Cattle To Disease The Mastitis Model Html
Therefore this study was presence of clots flakes blood and watery secretions.
Predisposing factors of mastitis in dairy farming. Palpatory pain changes in milk blood-mixed milk watery discharges flakes pus and variation in udder consistency were regarded as signs of clinical mastitis and all the physical examination procedures were conducted as per the guidelines of Quinn et al. Four different factors were signifi- veterinary costs and reduced milk yield Seegers et al. Parity concrete and rubber floor hand stripping after using machine milking dry cow therapy and routine cleaning of milking machines.
There were especially high prevalences of contagious udder pathogens and high SCC in alpine dairies. Predisposing factors in the management and environment cause mastitis by negatively influencing the local and systemic barriers and defence of the cow andor by increasing exposure of the udder to micro-organisms. Clinical mastitis causes a negative economic impact on dairy farms through abnormal milk deterioration of milk quality reduced production up to 70 milk discharge after treatment 9 treatment costs 7 labor premature culling 14 and death 5-7 whereas subclinical mastitis.
Clinical mastitis results in alterations of milk composition and appearance decreased milk production and the presence of the cardinals signs of inflam- mation pain swelling and redness with or without heat in infected mam- mary quarters. Poor sanitation increases multiplication of the bacteria causing mastitis. Compared with the large number of studies on CMS farms only a limited number of studies have been published on risk factors for mastitis on AMS farms.
Our study provided evidence of high prevalences of subclinical mastitis and information on risk factors of the disease in organically managed Swiss dairy herds. Predisposing factors for mastitis incidence highly depend upon type of breed stage of lactation management practices and awareness of the dairy farmers. Persson Waller et al.
Automatic milking systems AMS are installed on a growing number of dairy farms worldwide. Conditional probability results showed that the following variables had the highest probabilities relevant to the occurrence of clinical mastitis pathogens. Pulling also results in teat injury which further makes the animal to withhold milk.
Cantly associated with the occurrence of subclinical mastitis Huijps et al. In developed countries where bulk tank somatic cell counting is carried out routinely high. Risk factors like breed age parity lactation stage previous history of mastitis housing conditions milking hygiene and general management conditions.
Subclinical mastitis in lactating dairy cow to elucidate Subclinical mastitis was diagnosed based on the associated risk factors and to isolate and CMT results and the nature of coagulation and characterize the. The aim of this study was to identify farm level factors. Subclinical mastitis SCM occurs when both milk and mammary gland appear normal but somatic cell counts SCC is elevated to a level above 200000 cellsmL and this result in reductions in the amount and quality of milk Seegers et al2003.
And 200 and 286 in farm s with soil floor during the dry and wet seasons respectively. When milk left in teat canal it acts as culture medium for bacteria. The prevalence of mastitis was 306 and 585 in farms with brick-block floor.
The udder was examined clinically using visual then through. A total of 384 lactating cows were selected from small- medium- and large-scale production systems. Clinical and sub-clinical mastitis are the two major forms of the disease.
Scant literature is available on quantification of region-specific economic effects of subclinical form of mastitis where visible abnormalities such as udder swelling hardness of the affected quarter pain and. Wounds on teatsudder allow micro-organism entry into the udder. A case of mastitis.
Designed to estimate the prevalence of clinical and California Mastitis Teat CMT. Direct and indirect cost incurred during the control of clinical cases of mastitis together with prolonged subclinical mastitis reduces quantity and quality of milk produced and hence decrease smallholder dairy farmers income. Sub-clinical Mastitis This type of mastitis does not cause obvious visible changes to the milk but there may be some chronic inflammatory changes to the udder detected as hardness or knotty tissue on palpation of the affected quarter s.
Non-aureus staphylococci were the most frequently isolated pathogens from the clinical mastitis cases and causing most of the intramammary infections. Up to 10 cash back A cross-sectional study was carried out to determine the prevalence and risk factors of bovine mastitis caused by Streptococcus agalactiae from farms in and around Haramaya district eastern Ethiopia. Deyeng village in Kediri district is lowland region which is not common for dairy farming.
2003 reported that the incidence of milk leakage is higher on AMS farms than on CMS farms which increases the risk of mastitis. The odds of clinical mastitis were lower in herds where heifers were purchased in the last year old cows 4 y and quarters not showing teat injury. Management to support good udder health might be different on farms with an AMS compared with farms milking with a conventional milking system as risk factors for mastitis on farms using an AMS may differ.
High hygiene standards The person doing the milking must thoroughly wash their hands before milking. In total 100 quarters of milk samples from 100 cows were used for Bayesian network analysis. Mastitis in dairy cattle affected by many predisposing factors.
The dairy farms were physically inspected for cleanness handling milking procedures and other factors associated with mastitis. To control mastitis across the world it still remains an unconquered mountain. Bovine mastitis remains to be the most important disease facing smallholder dairy industry in Zanzibar.
Animals with large pendulus loosely hanging udder and long teats are more susceptible to mastitis. These factors are number of livestock climate social culture milk distribution systems farmers education farming management are important factors implicate subclinical mastitis case 8. California mastitis test CMT was used.
Currently Escherichia coli and Streptococcus uberis continue to be.

Milk Testing For Mastitis Detection In Dairy Herds

Tidak ada komentar